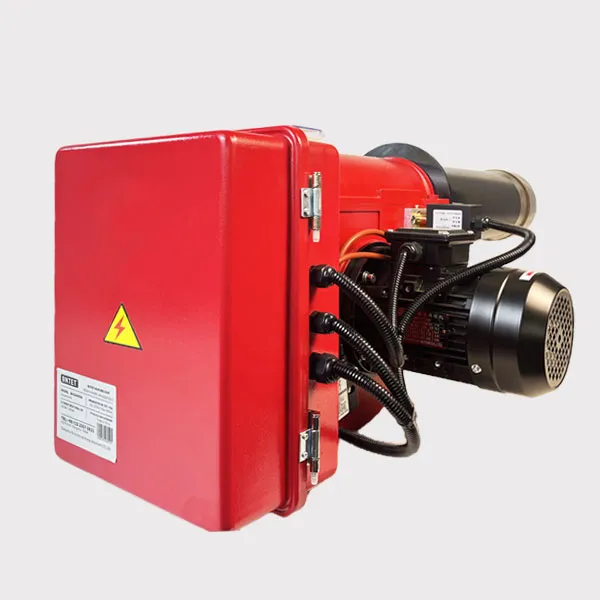
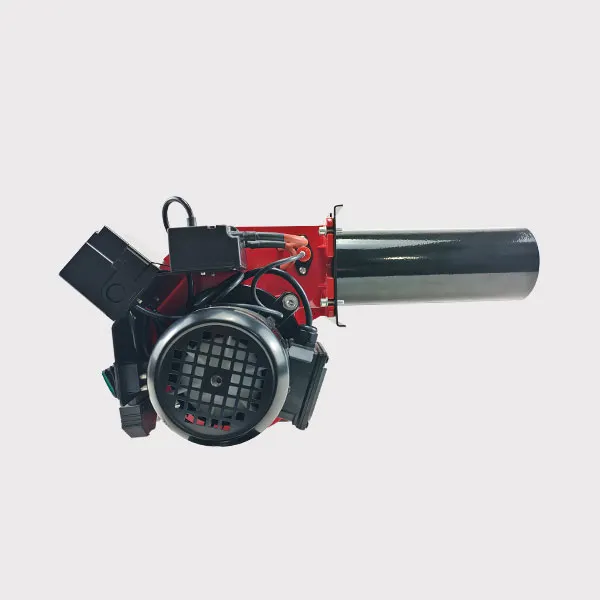
The main structure of boiler gas burner
2025-04-25 11:28:38
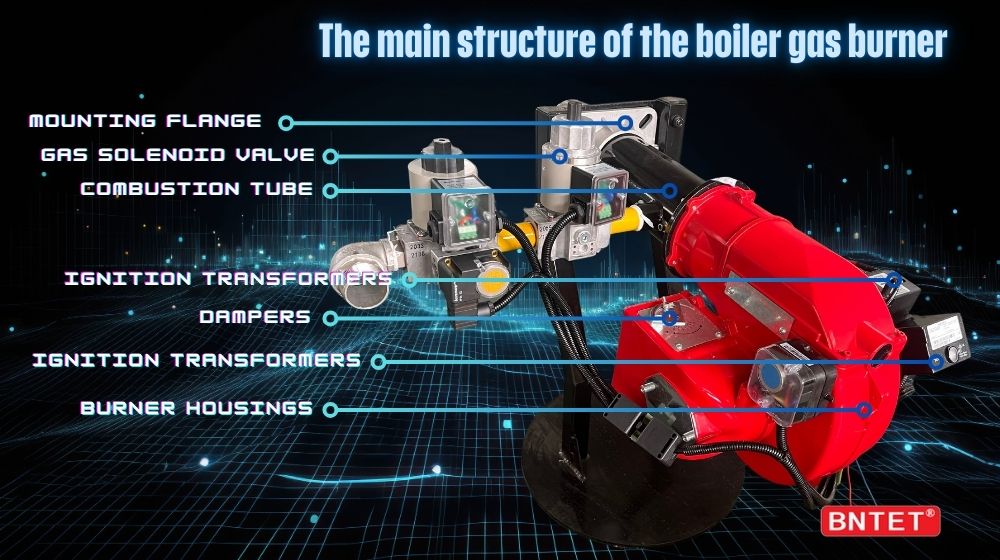
The boiler gas burner is one of the core components of the boiler system, responsible for mixing gas and air in a certain proportion and igniting to provide stable and efficient combustion. Its main structure includes the following key parts:
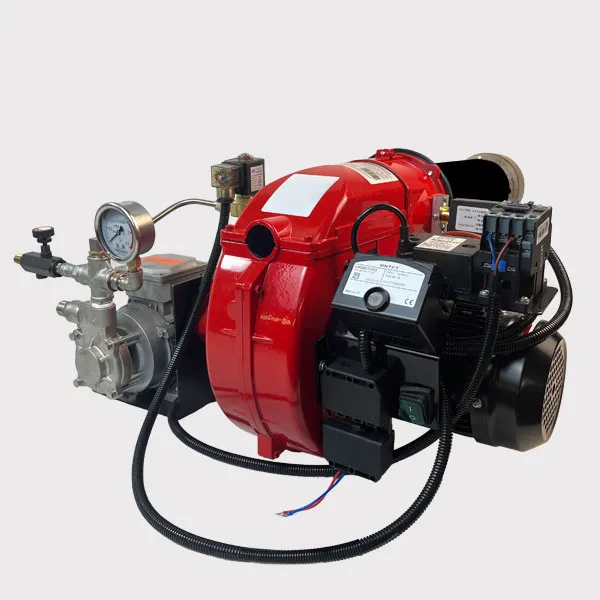
1. Gas Supply System
Gas solenoid valve: controls the on and off of gas to ensure safe gas supply.
Gas regulating valve: adjusts the gas flow to match different load requirements.
Gas filter: removes impurities in the gas to prevent clogging of the nozzle or valve.
Gas pressure gauge/sensor: monitors the gas pressure to ensure stable combustion.

2. Air Supply System
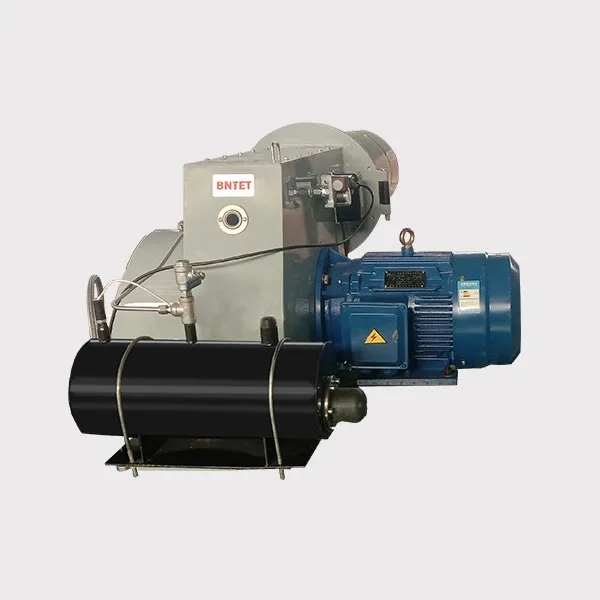
Blower: provides the air required for combustion and ensures sufficient wind pressure.
Damper adjustment device: manually or automatically adjusts the air flow to optimize the air-fuel ratio.
Air filter: prevents dust from entering the burner and affecting the combustion efficiency.
3. Burner Head
Nozzle: sprays gas and mixes it with air, affecting the flame shape and combustion efficiency.
Flame Stabilizer: Ensure flame stability and prevent flameout or flashback.
Combustion Chamber: Gas and air are mixed and burned here. Some burners are made of high-temperature resistant alloys.
4. Ignition System
Ignition Electrode: Generates electric sparks to ignite gas.
Flame Sensor: Monitors flame status (such as UV/IR sensor or ionization probe) to ensure safe operation.
Ignition Transformer: Provides high voltage electricity to generate sparks.
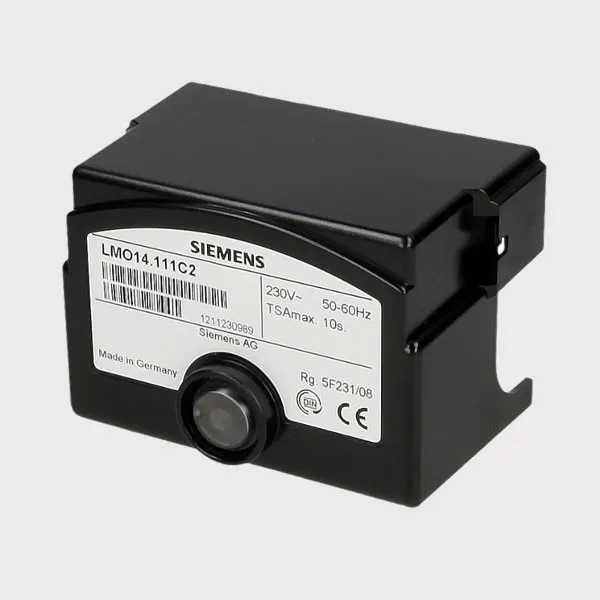
5. Control System
Combustion Controller: PLC or single-chip microcomputer control, adjusts the gas/air ratio, realizes automatic ignition, operation monitoring and fault protection.
VFD (optional): Adjusts fan speed to optimize combustion efficiency (applicable to variable frequency burners).
Human-machine interface (HMI): Touch screen or button panel for easy parameter setting and status monitoring.
6. Safety System
Gas leak detection: Some high-end burners are equipped with methane sensors to prevent gas leaks.
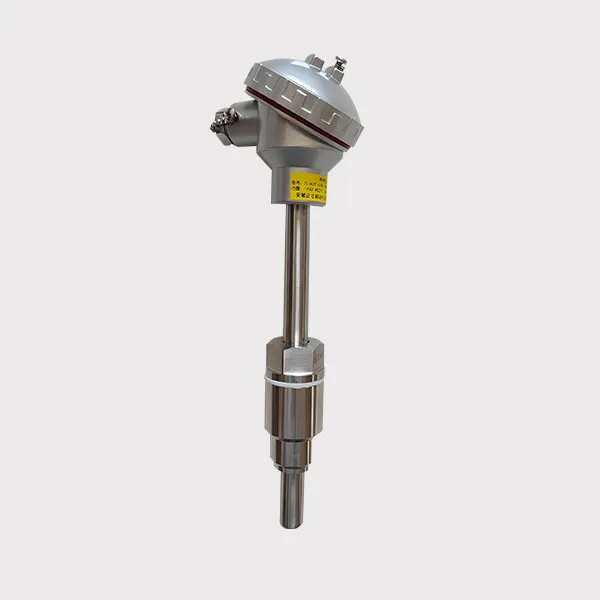
Over-temperature protection: Thermocouples or temperature sensors monitor the combustion temperature to avoid overheating.
Flameout protection: The flame detector monitors in real time and automatically cuts off the gas supply when the flame is out.
Air pressure switch: Detects the operating status of the fan to ensure normal air supply.
7. Housing & Accessories
Burner housing: Protects internal components and is usually made of heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials.
Flange/connector: Connects to the boiler furnace to ensure sealing.
Muffler (optional): Reduces combustion noise and is suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
Structural differences between different types of burners
Diffusion burner: Gas and air are mixed during the combustion process, with a simple structure and suitable for small boilers.
Premixed burner: Gas and air are fully mixed before combustion, with high combustion efficiency and low NOx emissions.
Staged burner: Use multi-stage combustion technology to further reduce pollutant emissions (such as low-nitrogen burners).
Summary
The structural design of boiler gas burners directly affects their combustion efficiency, emission level and safety. Modern burners tend to be intelligent, low-nitrogen, and equipped with more precise control systems to meet environmental regulations and energy efficiency requirements.
If you need a more detailed analysis of a certain part (such as low-nitrogen combustion technology, frequency conversion control, etc.), you can consult us. We can provide various burner customization services.







