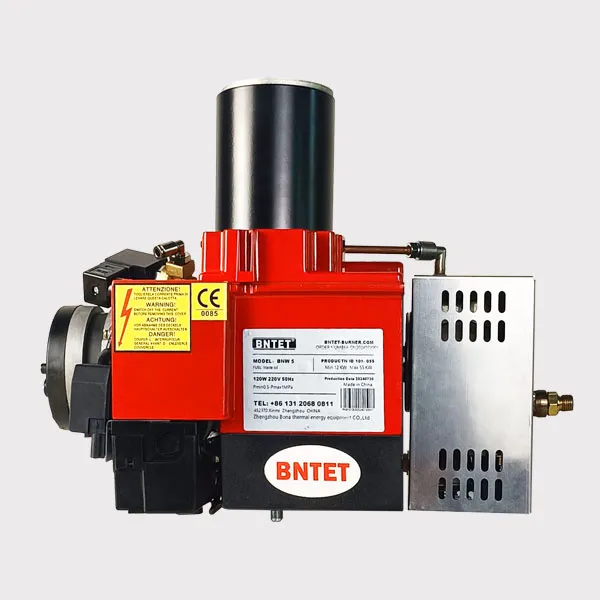
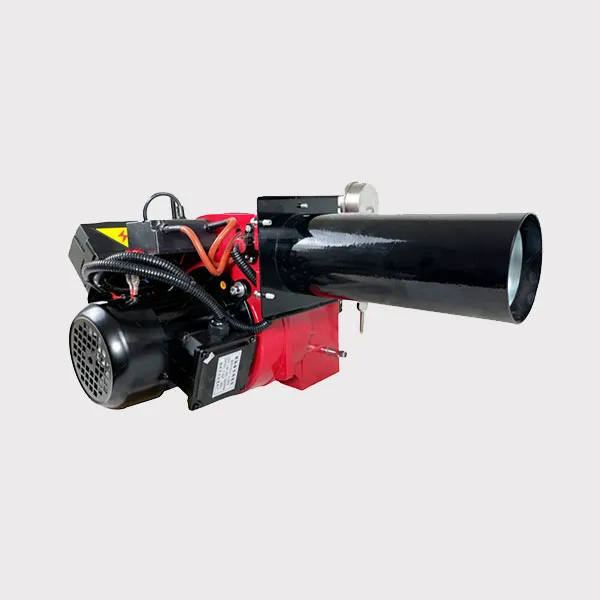
Why fire tube boilers must use long flame narrow diameter burners
2025-02-06 17:45:11
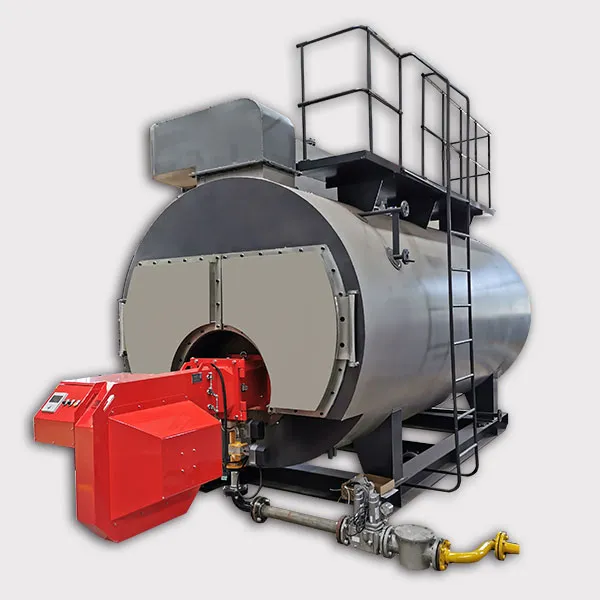
Fire tube boilers utilize long flame, narrow diameter burners for several important reasons related to their design, efficiency, and operational performance. Here's a detailed explanation:
1. Heat Transfer Efficiency
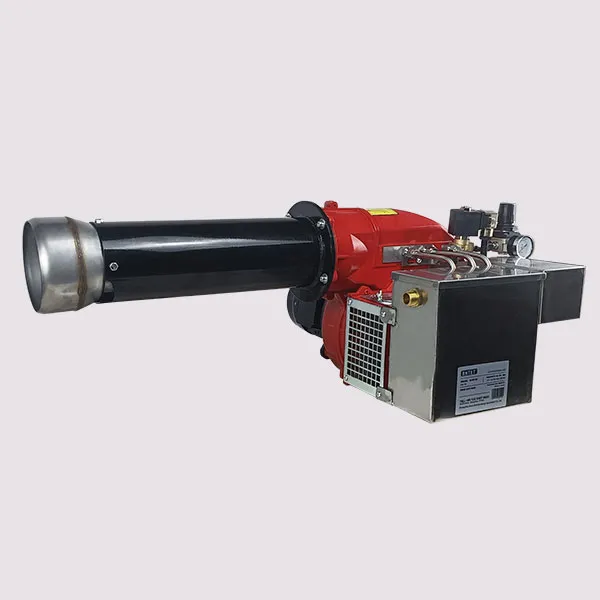
Long Flame: The long flame produced by these burners allows for a larger surface area for heat transfer. This extended contact time between the hot gases and the water in the tubes enhances the boiler's overall efficiency.
Narrow Diameter: The narrow diameter of the burner helps to focus the flame, ensuring that the heat is concentrated and directed effectively into the fire tubes. This maximizes the heat transfer to the water or steam.
2. Combustion Stability
Stable Flame: Long flames provide a more stable combustion process. The design helps maintain a consistent flame shape and size, which is crucial for achieving uniform heating and preventing fluctuations in temperature.
Reduced Emissions: A stable flame results in more complete combustion of the fuel, reducing the formation of unburned hydrocarbons and lowering emissions.
3. Pressure and Flow Dynamics
Narrow Flame Spread: The narrow flame spread allows for better control of the combustion process. This is particularly important in fire tube boilers, where maintaining specific pressure and temperature conditions is essential for efficient operation.
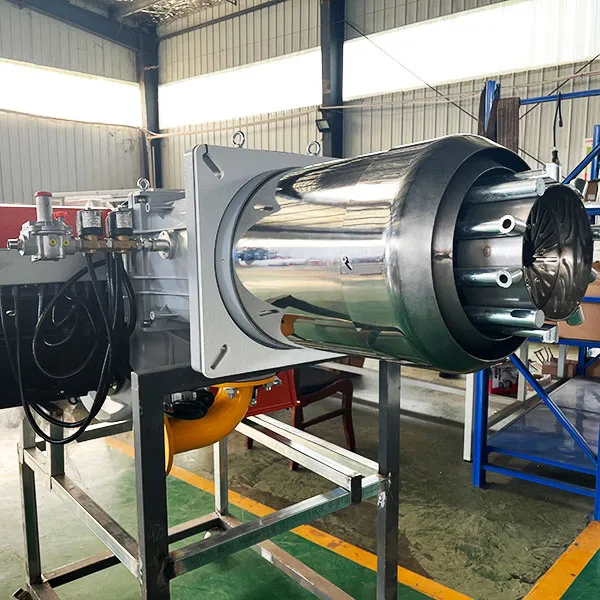
Effective Air-Fuel Mixing: The design promotes better mixing of air and fuel, leading to more efficient combustion and reducing the likelihood of soot formation.
4. Space Constraints
Compact Design: Fire tube boilers are often designed to be compact. Long flame, narrow diameter burners fit well within these constraints, allowing for effective heating without requiring excessive space.
Installation Flexibility: The design of these burners allows for easier installation in various boiler configurations, making them versatile for different applications.
5. Safety Considerations
Controlled Flame Length: Longer flames can be designed to burn within a controlled environment, reducing the risk of flame impingement on boiler surfaces, which can lead to overheating and potential damage.
Reduced Risk of Backfire: The narrow design minimizes the risk of backfire, which can occur with wider flames that may extend into the burner assembly.
Conclusion
The use of long flame, narrow diameter burners in fire tube boilers is essential for optimizing heat transfer, ensuring combustion stability, and enhancing operational efficiency. This design choice helps to meet the specific requirements of fire tube boilers while also addressing safety and environmental concerns.







